A Chinese visa is a permit issued by visa authorities of the People’s Republic of China in accordance with its laws and regulations to a foreign citizen for entry into, exit from or transit through Chinese territory. The Chinese visa authorities will issue a diplomatic visa, courtesy visa, service visa or ordinary visa according to the foreign citizen's status, purpose of visit and type of passport.

Basic Requirements
Passport
Original passport that is valid for at least another 6 months with at least one blank visa page, a photocopy of the passport's information/photo page and emergency contact page. The previous old passport, if available, is required to be submitted; if the old passport is lost, or the applicant never holds a passport before, please make a clear statement in the item 3.7 of the Visa Application Form.
Visa Application Form
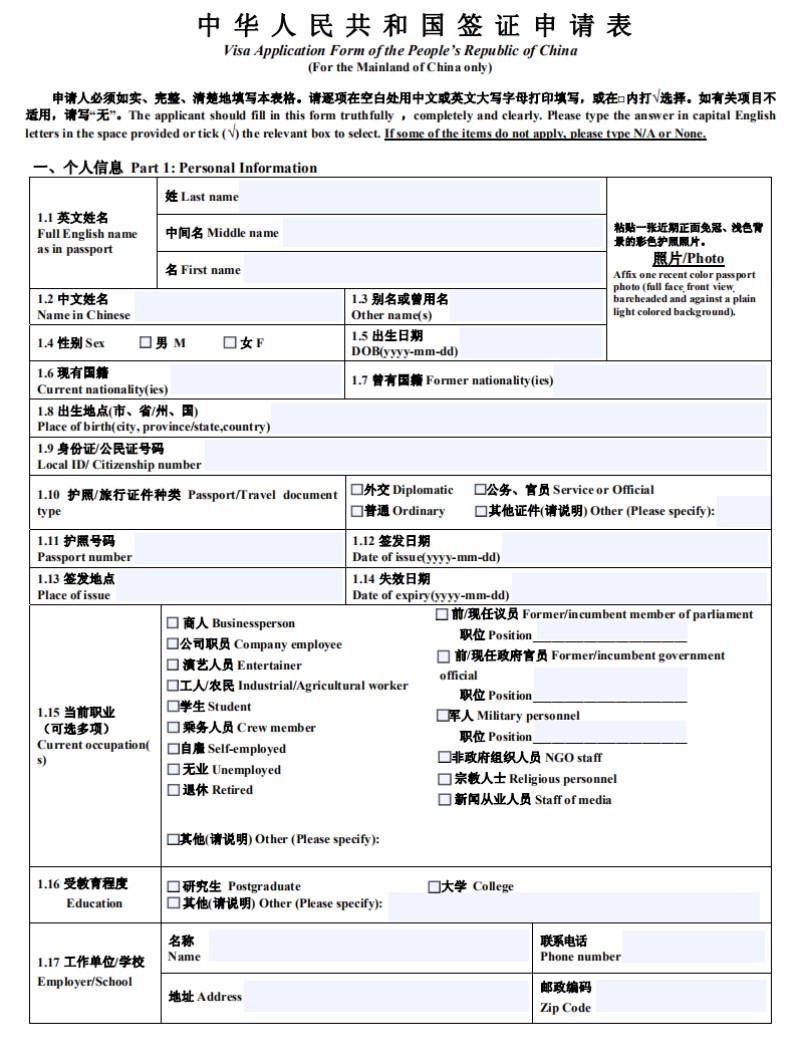
Please submit truthfully completed and signed Visa Application Form of the People's Republic of China. Please type the answer in capital English letters in the space provided. Do not leave any field blank. Type N/A if the item does not apply. Application form of minors must be signed by their parents or legal guardians.
Note: Please fill in the visa application form faithfully, completely and clearly, or possibly your visa application will be refused and accordingly make your oversea trip protracted.
Photo
Please provide 2 color photos and affix one of the photos on the Application Form. The photo should be recent (within 6 months), front view, white background, in 48mm x 33mm size without head covering. Stapled/taped/clipped/detached photos will not be accepted.
Do I need a Chinese Visa?

Generally, most foreigners traveling to mainland China, whether for business or leisure travel, need visas. It is very difficult to apply for a Chinese port visa at the Chinese border entry point. However, some cities and regions in China are visa free in some cases.
Holders of ordinary passports issued by the following 17 countries do not need a visa to enter China as long as their trip does not last longer than the visa-free period listed below.
90 days: Bosnia and Herzegovina, San Marino
60 days: Mauritius
30 days: Bahamas, Barbados, Belarus, Ecuador, Fiji, Grenada, Qatar, Serbia, Seychelles, Tonga, United Arab Emirates
15 days: Brunei, Japan, Singapore
Visa Types
According to foreigners' status, their purposes for coming to China and the passport type, the Chinese visa issuing authorities may separately issue them the diplomatic visa, courtesy visa, service visa or ordinary visa. For the ordinary visa, there are eight categories, separately represented by eight Chinese phonetic letters (C, D, F, G, J-1, J-2, L, X, Z) as the visa code.
C Visa (Crewmember Visa): Issued to crewmembers on international aviation, navigation and land transportation missions and their accompanying family members.
D Visa (Residence Visa): Issued to foreigners who are going to live in China permanently.
F Visa (Business/Visit Visa): Issued to foreigners who are invited to China for a visit, research, lecture, business, scientific-technological and cultural exchanges or short-term advanced studies or intern practice for a period of less than six months.
G Visa (Transit Visa): Issued to those people who transit through China.
L Visa (Tourist Visa): Issued to those who enter China temporarily for touring, family visiting or other personal affairs (multiple-entry is not granted for this category).
X Visa (Study/Student Visa): Issued to foreigners who come to China for study or intern practice for a period of six months or above.
Z Visa (Work Visa): Issued to foreigners who are to take up a post or employment in China, and their accompanying family members.
J Visa (Journalist Visa)
J-1 Visa issued to foreign journalists who are posted to China for at least one year.
J-2 Visa issued to foreign journalists who are on temporary assignment in China.










